China’s Climate Cooperation Smokescreen: A Roadmap for Seeing Through the Trap and Countering with Competition
Gabriel B. Collins and Andrew S. Erickson, China’s Climate Cooperation Smokescreen: A Roadmap for Seeing Through the Trap and Countering with Competition (Houston, TX: Baker Institute for Public Policy, Rice University, 31 August 2021).
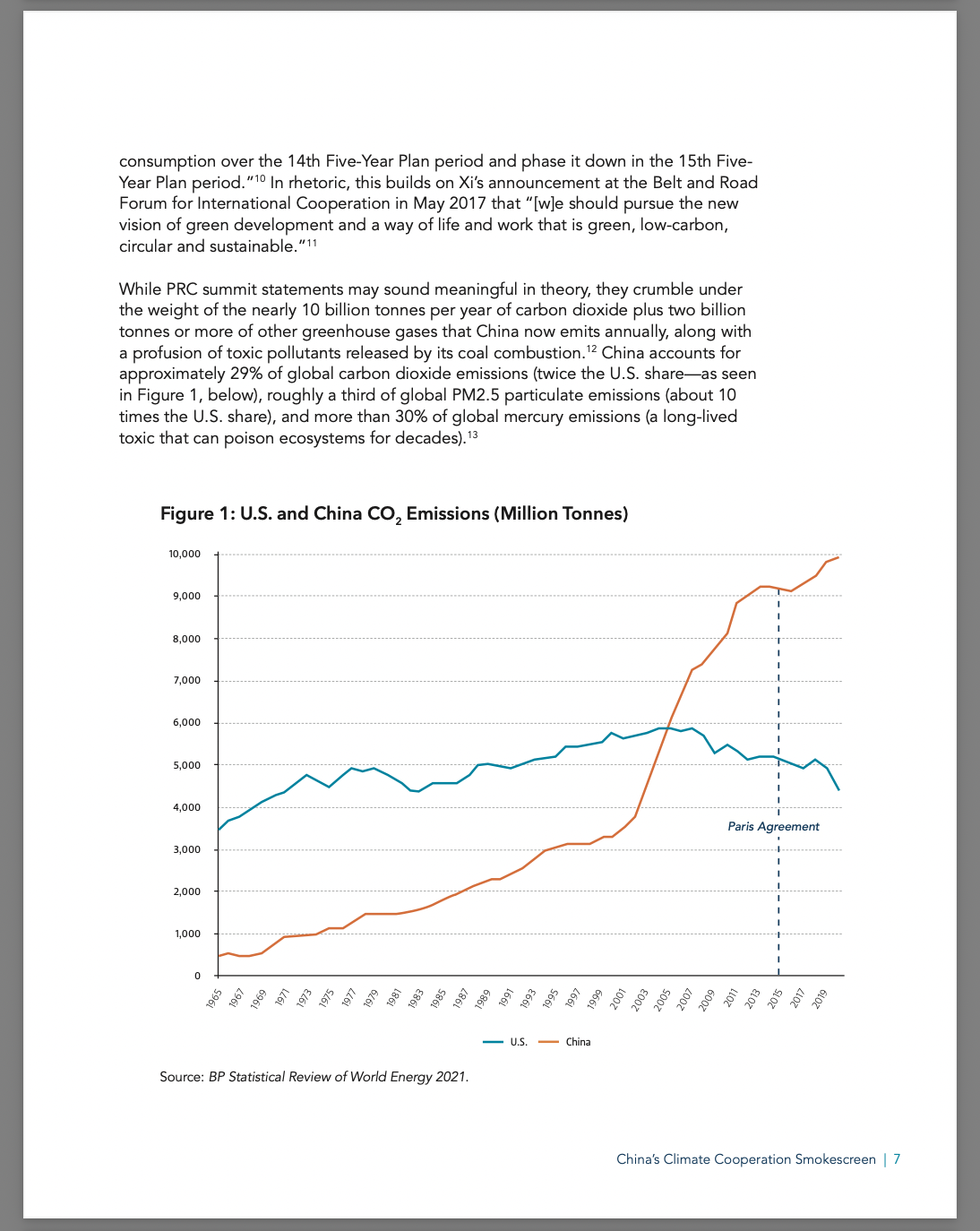
China accounts for approximately 29% of global carbon dioxide emissions but has an “abiding commitment to coal,” write the authors. Their report outlines a climate competition strategy — specifically, leveraging the threat of carbon taxation — to incentivize a timely transformation in Beijing and provide a viable pathway to preserving the atmosphere and oceans for future generations.
KEY POINTS
- Beijing’s quest for political leverage at home and abroad overrides its concern for the climate.
- Leading-emitter China pushes to link its political priorities to others’ climate priorities.
- When foreign supplicants collide with the Chinese Communist Party’s (CCP) self-interest, they will pay with both up-front concessions and wasted time, during which critical climate systems could be pushed beyond the point of no return.
- This is a major danger facing the administration of President Joe Biden.
- Real pro-climate progress requires fundamentally shifting the CCP’s calculus by actually altering the economic bottom line on which its power hinges.
- Climate competition—specifically, leveraging the threat of carbon taxation—is the only Archimedean lever powerful enough to incentivize a timely transformation.
- This paradigm-shifting approach would curtail China’s latitude for exploitative geopolitical maneuvering and empower sidelined reformers.
- Climate competition supports a whole-of-coalition “race to the top” for pro-climate actions, with the EU carbon border tax proposal an extant example.
- Crucially, it could also anchor the bipartisan domestic support necessary to keep Washington a reliable long-term climate leader and partner of choice.
- Finally, it offers on-ramps for China itself to engage more decisively on climate change both domestically and internationally, and to benefit accordingly.
- No silver bullet exists, but climate competition offers the most viable pathway to preserving the atmosphere and oceans for future generations.
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
This report expands on an essay the authors published in the May/June 2021 issue of Foreign Affairs.1 It provides additional explanation of how President Biden and his team can, and must, avoid two important foreign policy pitfalls: (1) entrapment in climate cooperation negotiations with Beijing that compromise vital American interests up front without corresponding Chinese concessions (let alone reciprocation), and/or (2) economic self-sabotage if the United States makes great climate sacrifices unilaterally, but the People’s Republic of China (PRC) fails to do its part. To help manage these looming risks, this report provides a roadmap to guide U.S. policymakers through Beijing’s climate cooperation smokescreen and into emissions-constraining competition with China.
The most viable path to sustainable biosphere security entails first competing with China by rallying a climate coalition whose alignment Beijing will ultimately seek by making more credible commitments than Washington itself could prompt unilaterally. It is time for a signature American initiative that brings allies and partners from the world’s largest market bloc into a massive U.S.-led movement. This conglomerate of the committed can generate the one Archimedean lever too powerful for Beijing to ignore. The fulcrum: carbon taxation and border adjustment taxes that would impose a heavy cost on future PRC climate destruction, directly impacting not only China’s international reputation, but—far more consequentially—its core growth model. No amount of domestic repression, propaganda, or recalcitrance could hide or offset an undermining of that growth model, a cornerstone of Chinese Communist Party (CCP) legitimacy.
To that end, this report first explains the empirical roots of China’s contradictory stances on carbon and greenhouse gas emissions and how Beijing’s attempts to extract concessions actually reflect a fundamental weakness in its competitive position on carbon. It then articulates a set of actionable, forward-leaning policy ideas aimed at regaining the climate initiative through a novel course of action—competition. A proactive whole-of-coalition effort can incentivize Beijing
to defend its global diplomatic, economic, and industrial competitive position in ways that unilateral supplication simply cannot—with much greater prospects for success. Only such a realignment has the potential to bring China to the table for productive negotiations rather than the distracting or extractive ones it currently pursues.
Our report leverages extensive empirical evidence to help explain China’s abiding commitment to coal and the CCP interests that drive the ongoing obfuscation in its climate rhetoric.2 For policymakers, it also outlines a climate competition strategy to incentivize Beijing to become a positive force for climate progress, rather than a selfish spoiler. While competition is presently not a universally popular approach, it offers Washington’s most plausible route (in concert with allies and partners) to help fundamentally recalibrate China’s incentive structure in the interests of global biosphere security. Competition is also the pathway most congruent with achieving emissions reductions and reshaping the international climate diplomacy paradigm, while also making progress on domestic emissions reduction. While this report emphasizes competition, it also leaves open on-ramps to simultaneous avenues for engagement, should Beijing finally elect to participate in good faith.
SAMPLE CONTENT FROM REPORT:
Gabriel Collins, J.D.
Baker Botts Fellow in Energy & Environmental Regulatory Affairs, Rice University’s Baker Institute for Public Policy
Andrew S. Erickson, Ph.D.
Professor of Strategy, China Maritime Studies Institute, Naval War College