Mind The Gap: How China’s Civilian Shipping Could Enable a Taiwan Invasion
Timely, relevant, and predictive analysis by brilliant analyst Thomas Shugart. Best read together with (1) the pathbreaking, widely-cited article by Conor Kennedy that he mentions, and (2) the Quick Look summary of the CMSI Conference to which both superstars made critical contributions. I’ve linked all three pieces here; please scroll down to access all now!
Thomas Shugart, “Mind The Gap: How China’s Civilian Shipping Could Enable a Taiwan Invasion,” War on the Rocks, 16 August 2021.
Recent months have seen much discussion of the “Davidson Window” — the idea, based on recent commentary by the then-commander of U.S. Indo-Pacific Command, Adm. Philip Davidson, that China could take military action against Taiwan in the next six to 10 years. Some within the defense commentariat accused Davidson of “sloppy exaggeration,” that he was “simply wrong as a matter of fact” (though perhaps some critics should consider that a combatant commander may have access to a different set of facts than they do). While others took his warning more seriously, there have been good reasons to question whether China could successfully subjugate Taiwan any time soon. Among these is that China has appeared to lack the amphibious transport capacity necessary to successfully conduct a cross-strait invasion. However, assessments of China’s amphibious sealift capability have typically focused on its navy’s dedicated amphibious assault ships, and have largely discounted the ability of China’s civilian merchant shipping to contribute to an invasion — especially in its initial stages. This approach does not take sufficient account of the emerging and ongoing integration of substantial portions of China’s merchant marine into its cross-strait assault forces. When civilian shipping is included in an assessment of China’s cross-strait sealift capability, Davidson’s warning gains added credibility. … … …
***
Conor Kennedy, “Ramping the Strait: Quick and Dirty Solutions to Boost Amphibious Lift,” Jamestown China Brief 21.14 (16 July 2021).
Introduction
The threat of the People’s Liberation Army (PLA) using military force to coerce or perhaps launch an amphibious invasion of Taiwan has received significant attention in the past year. Meanwhile, the recent commissioning of the PLA Navy’s first Type-075 amphibious assault ship has further highlighted China’s developing amphibious capabilities (South China Morning Post, May 9). At the same time, the apparent shortage of amphibious lift required to execute large-scale landing operations leaves many wondering whether China is serious about its threats against Taiwan. The U.S. Department of Defense’s 2020 China Military Power Report notes the PLA’s focus on ocean-going amphibious platforms rather than a large fleet of traditional landing ships and craft suggests that a direct beach-assault operation is less likely at the moment (Office of the Secretary of Defense, September 1, 2020).
But the PLA may have other plans for transporting troops and equipment across the Strait: the growing capabilities of its merchant roll on-roll off (RO-RO) ships (CMSI, December 6, 2019). These are vessels equipped with built-in ramps that enable wheeled and tracked cargo to load and offload under their own power. Such ships have the potential to deliver a significant volume of force, providing access to port terminals or other lighterage is available. They do not, however, provide solutions for launching waves of amphibious assault forces, for which dedicated landing ships are still lacking. Among the numerous critical components necessary for a successful cross-Strait landing, a failure to secure landing areas for follow-on forces in the initial assault would bring the entire endeavor to a screeching halt, likely inflicting severe costs on the part of the aggressor and resulting in a withdrawal.
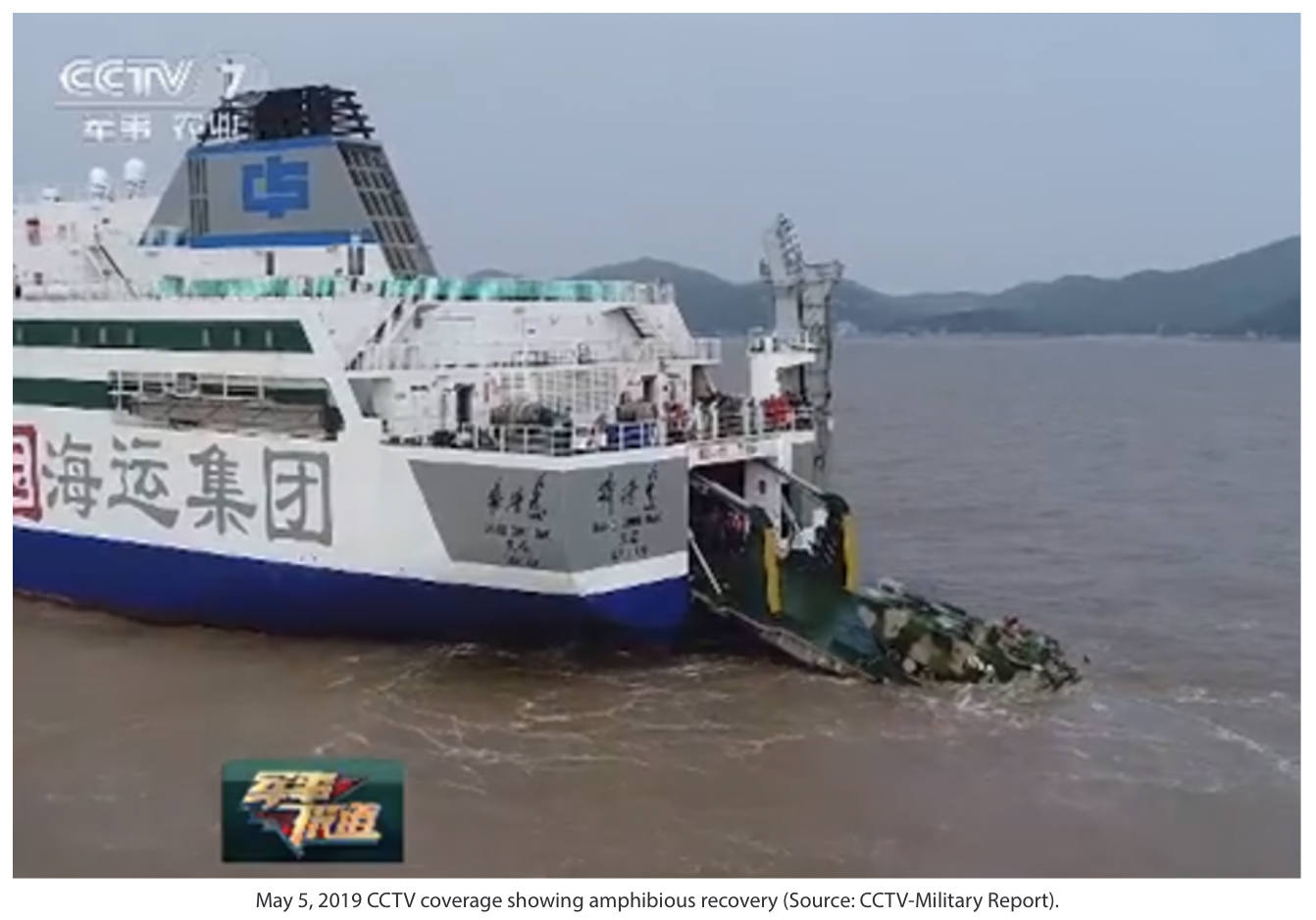
For China’s RO-RO ships to support an amphibious assault scenario, their ramps would need to be capable of in-water operations to launch amphibious combat vehicles. This capability appears to have been publicly demonstrated in the summer of 2020 by the PRC-flagged vessel Bang Chui Dao (棒棰岛), a 15,560-ton RO-RO owned and operated by COSCO Shipping Ferry Company (COSCO Shipping Ferry, accessed June 24). This article describes a new ramp system observed on this ship during a recent exercise and discusses its implications for PLA amphibious capabilities in a cross-Strait landing.
New Ramp System Demonstrated in Amphibious Landing Exercises
During the peak of summer training in 2020, the 1st Marine Brigade of the PLA Navy Marine Corps (PLANMC) mustered all personnel and equipment (全员, 全装, quan yuan, quan zhuang) for day and night landing exercises in amphibious training areas off the coast of Guangdong Province. These exercises featured night-time mobilization and assembly, embarkation, obstacle clearance, amphibious assault landings, and artillery and air defense training (js7tv.cn, August 2, 2020). They also included the use of a new ship to carry these forces to their training area.
On July 10, the Bang Chui Dao, which usually runs ferry routes across the Yellow Sea and Bohai Gulf, arrived in Zhanjiang (湛江) to join the PLANMC exercise. It took on 1st Brigade troops, trucks, and Type-05 amphibious armored vehicles at the Southern Theater Navy’s 6th Landing Ship Flotilla loading dock (CCTV, August 3, 2020). According to automatic identification system (AIS) transmission data of the vessel’s movements, the ship departed Zhanjiang just before 10:00 AM local time and arrived off Tangxia (塘霞), an amphibious training area in Dianbai County (电白区), at almost 4:00 PM. AIS data indicates that it likely began launching vehicles 4 to 5 kilometers (2.5 to 3.1 miles) offshore without dropping anchor. Video of a vehicle launching shows the ship was likely running slow into the wind to maintain a lee astern; it appears to have maintained bare steerage while drifting to the southeast at half a knot until offloading was completed and then departed for nearby Shuidong Harbor at around 4:48 PM.[1] After being moored dockside overnight and well into the next day, the ship then left for the Shuidong anchorage on the evening of July 11. It returned to Zhanjiang in the afternoon of July 12, presumably to offload PLANMC forces. Although it is unclear how many PLAN landing ships took part, at least one Type-073A landing ship likely participated (CCTV, August 3, 2020). … … …
***
Quick Look—CMSI’s 4–6 May 2021 Conference: “Large-Scale Amphibious Warfare in Chinese Military Strategy” (Taiwan Strait campaign focus)
The Naval War College China Maritime Studies Institute (CMSI) has just released the Quick Look summary of its 4–6 May 2021 Conference on “Large-Scale Amphibious Warfare in Chinese Military Strategy.”
***Please kindly note that this Quick Look summary DOES NOT represent the views of any one individual participant, or assessments of the U.S. government.***
This conference seeks to increase our understanding of large-scale PLA amphibious warfare. We focus on the role of major amphibious operations in Chinese strategy to protect Beijing’s so-called “core interests,” namely a Taiwan Strait campaign. After putting the strategy in historical context, we assess PLA operational doctrine for major amphibious operations, recognizing that such operations are certain to be undertaken with close coordination among PLA air, sea, missile, and ground components. This conference evaluates how Chinese large-scale amphibious warfare would fit within a larger hypothetical campaign. The conference concludes with a discussion of the possible significance of major PLA amphibious operations for U.S. naval strategy.
QUICK LOOK REPORT
“LARGE-SCALE AMPHIBIOUS WARFARE IN CHINESE MILITARY STRATEGY”
BACKGROUND
From 4–6 May 2021 CMSI held a virtual academic conference on the topic of large-scale PLA amphibious warfare (i.e., a Taiwan invasion scenario). The event was unclassified. The roughly 160 attendees were all U.S. citizens. Participants included experts from government, academia, and U.S.-based think tanks. Panel topics included 1) Historical Cases Informing Chinese Amphibious Warfare, 2) The Joint Amphibious Force, 3) Enablers of Amphibious Warfare, 4) Pre-Assault Conditions, 5) Scenario Factors, and 6) Implications. This summary does not represent the views of any one individual participant, or assessments of the U.S. government.
KEY FINDINGS
- China has a political strategy for unification with Taiwan, with an important but subordinate military component.
- Xi and the CCP seek to resolve the “Taiwan problem” on terms they could call “reunification.”
- Beijing continues to prefer long-term progress by non-war means, such as military, economic, and political coercion.
- China keeps strengthening relevant capabilities.
- Lacking the geographic and policy constraints facing Washington, Beijing has long emphasized missiles.
- The PLA is developing both the sensors and shooters (surface-to-air missiles, advanced fighter aircraft, etc.) needed to vie for air superiority over the Taiwan Strait.
- With probably the world’s most potent at-scale mine delivery capability, China appears to vastly exceed the U.S., Japan, and Taiwan. It has also invested heavily in MCM capabilities.
- The PLA is developing new technologies (e.g., UAVs) to support a potential invasion force.
- China retains many weaknesses.
- Despite sweeping reforms, PLA jointness—essential to success in a Taiwan invasion—suffers persistent limitations, including apparent lack of joint training among special operations communities.
- Despite dramatic expansion since 2017, the PLAN Marine Corps does not seem to be optimizing itself for a traditional amphibious landing against Taiwan.
- Operations to protect China’s expanding overseas interests appear to be a major focus of its development.
- PLA helicopter forces suffer enduring limitations, particularly in overall readiness; and in operational capacity under combat conditions, including air-ground integration.
- Taiwan’s natural geographic defenses (Strait, weather, tides, currents, mudflats, coastal terrain) offer formidable protection, despite a mounting China-Taiwan military imbalance.
AREAS OF CONSENSUS
- Lacking in major modern-era successes of its own (beyond its seizure of Hainan and Yijiangshan Islands, etc.), the PLA has carefully studied foreign experiences with amphibious operations and incorporated relevant lessons.
- A cross-Strait invasion remains tremendously difficult and risky for the PLA, despite a growing military imbalance across the Strait.
- China has clearly attempted to emulate and incorporate major “gold standards” of U.S. doctrine, terminology, and forces.
- China recognizes sea and air control as prerequisites for a successful invasion.
- China is pursuing comprehensive capabilities through incorporation of all possible forces, including a major emphasis on Maritime Militia and civilian logistics.
- The PLA is attempting to boost the realism of its amphibious training/exercises.
- The PLA currently lacks the required amphibious lift, logistics, and materiel for a robust cross-Strait invasion and shows no urgency to achieve it.
- China is building large amphibious vessels, but these appear to be designed to support overseas operations, not a cross-Strait invasion per se.
- China has not yet built the large numbers of LSTs and LSMs that would support a conventional invasion of Taiwan.
- Indeed, its inventory of those more essential, “expendable” vessels is arguably smaller than it was a decade ago.
- Thus, a major invasion today would require heavy reliance on civilian assets.
- The PRC is unlikely to achieve a major element of surprise.
AREAS OF DEBATE
- Whether the PLA might preemptively threaten strikes against—or seizure of—offshore islands (Kinmen, Matsu, Pratas, Penghu Islands) as a means of coercion short of attempting to invade Taiwan’s main island?
- Extent to which the PRC would have to exploit a limited number of predictable landing points on Taiwan’s main island, where Taiwan could prepare for defense prior to conflict?
- Whether the PLA seeks to prioritize large-scale beach landings or seizure of Taiwanese ports to facilitate invasion?
- Citing PLA textbooks, one presenter argued that major ports are the key/priority.
- Several presenters contended strongly that the PLA will likely be unable to successfully conduct a large-scale cross-Strait invasion until it masters what the U.S. military terms Joint Logistics Over-the-Shore (JLOTS).
- Whether Beijing could effectively use civilian assets to support a cross-Strait invasion?
- Most participants concluded that current ability is inadequate.
- One presenter argued strongly that Maritime Militia forces might operate mobilized civilian shipping as a “just-good-enough” logistical backbone.
IMPLICATIONS
- The PLA has achieved tremendous progress in developing many of the capabilities needed for a cross-Strait invasion. The threat posed to Taiwan is grave.
- Nevertheless, the inherent challenges and risks remain sufficiently high for Xi and the CCP that Taipei, Washington, and Tokyo can continue to deter—or, in a worst case, frustrate—an invasion.
- Key PRC sensors are far less numerous than key PRC shooters, and hence a better single-point-failure target for limited U.S. and allied fires.
- Taiwan must redouble its efforts to build A2/AD “porcupine” capabilities grounded in its natural defenses.
- U.S. planners must consider the possibility of the PRC improvising in just-good-enough-for-long-enough fashion to attempt to pursue basic political objectives, particularly if events or trendlines “force” Xi’s hand.