Glad to Speak with The Wire China for “Deep State, Inc.” Cover Story—On China Sam Enterprise Group’s Fishy Plans for Strategic Solomon Islands
Alex W. Palmer, “Deep State, Inc.,” Cover Story, The Wire China, 21 February 2021.
A nixed deal offers a rare window into how Chinese companies often work in tandem with, and sometimes on behalf of, Beijing.
Peter Kenilorea Jr. was scrolling through Facebook one afternoon in September 2019 when he came across a photo that caught his attention. It was a snapshot of an agreement between a provincial governor in the Solomon Islands, where Kenilorea lived, and executives from a company called China Sam Enterprise Group. The agreement appeared to grant the Chinese conglomerate exclusive development rights to Tulagi, one of the Solomon Islands, for at least 75 years. It was a leak, and an alarming piece of news for Kenilorea. Despite serving as the deputy opposition leader in the Solomon Islands parliament and chairman of its foreign relations committee, he knew nothing about the deal. When Kenilorea began commenting on the photo on Facebook, the original poster sent him a private message that included the full text of the agreement. The more Kenilorea read, the more he found troubling: the agreement was vague in detail and expansive in scope. It offered the Sam Group unusually preferential … …
In geopolitics, size matters, but so does location. Andrew Erickson…says the combined landmass of the Pacific islands is miniscule in a region where the Pacific covers 64 million square miles but they offer a foothold to a rising power. In that context, even tiny islands are viewed as critical to China, which is building a blue water navy and seeking to project power throughout the Pacific.
“Whether or not history rhymes, geography certainly endures,” Erickson says. “Long after World War II, the Solomons remain one of the Pacific’s limited number of island groups, and Tulagi one of its few natural deep water harbors.” … … …
RELATED ANALYSIS—THE PACIFIC “ISLAND CHAINS” IN COMPARATIVE HISTORICAL PERSPECTIVE:
Andrew S. Erickson and Joel Wuthnow, “Why Islands Still Matter in Asia: The Enduring Significance of the Pacific ‘Island Chains’,” The National Interest, 5 February 2016.
The Western Pacific “island chains” are a persistent feature of Asia’s maritime geography. While their underlying fundaments remain constant, their specific strategic importance has evolved over time. Different major powers have thus interpreted, then re-interpreted and re-evaluated, the value of particular islands, the role they play in national military strategy, and their operational significance in a warfighting context. Chinese naval strategists such as former naval commander Admiral Liu Huaqing have devoted considerable attention to the island chains since the mid-1980s, examining how and where the island chains can hinder or support China’s maritime goals. Yet Chinese strategists are hardly unique in their efforts—military theorists and planners from Germany, Japan and the United States have all pondered the geopolitics of the islands and archipelagos of the Western Pacific, during both peacetime and wartime. To understand the progression of Chinese views, and more recent debates among U.S., Japanese and Chinese strategists, we must trace this lineage of strategic ideas that stretches back more than a century.
Foreign Imperial Origins
The earliest known inklings of island chain-related concepts are intertwined with imperial Germany’s Pacific involvement at the turn of the twentieth century, just as the United States was taking possession of Spain’s previous colonial Pacific territories of Guam and the Philippines. Germany’s tenure as a Pacific colonial power—having acquired the Mariana Islands; and the Caroline Islands, including Palau; from Spain in the aftermath of the Spanish-American War of 1898—coincided with the early writing career of Major General Karl Ernst Haushofer. Serving as a military attaché to Japan from 1908 to 1910, Haushofer was preoccupied with the geopolitics of the Pacific, penning several books on the subject. He regarded the “offshore island arcs” of what he termed the “Indo-Pacific realm” as important geopolitical features providing a useful “protective veil” sheltering continental powers such as China and India.
Japan, for its part, was already a major Pacific sea power at the turn of the twentieth century, having defeated the Chinese Navy and seized Taiwan in 1895. As its maritime strength increased, Tokyo gave careful attention to the strategic value of different islands and archipelagos in the Western Pacific. During World War I, a Japanese expeditionary force wrested control over several Micronesian islands from imperial Germany. These were not only useful stepping stones in Japan’s “southward turn,” focused on exploiting Southeast Asia’s economic and natural resources, but also served as a valuable strategic buffer. In particular, control over Micronesia (chiefly the Mariana, Marshall, and Caroline islands; the last, notably, including Palau) was seen as a hedge against the possibility that the United States would use its bases in Guam and on the Philippines to threaten Japan in a future conflict.
U.S. military theorist Milan Vego explains how Japan took steps to solidify its control over Micronesian islands in the decades following World War I. Vego observes that the Japanese government embarked on a significant settlement and economic campaign during the 1920s and 1930s. The number of Japanese settlers on the islands eventually outnumbered the native islanders. In 1935, Vego notes, Japan withdrew from the League of Nations and its islands became “closed territories,” with Westerners restricted from entry.
At the outset of World War II, the Imperial Japanese Navy engaged in a series of lightning-fast island seizure operations, landings, and fortifications. This included operations to seize both Guam and Wake Island from the United States. During the middle of the war, Japanese forces sought control over other islands within the Second and Third Island Chains, including the Solomon Islands and as far as the Aleutian Islands off the coast of Alaska. Although many islands formerly in Japanese possession passed to the United States the Soviet Union as a result of the war, Japan eventually regained control over key components of the First and Second island chains, including the Ryukyu and the Ogasawara islands.
Japanese concerns over U.S. island possessions in the Western Pacific following the Spanish-American War were mirrored by evolving U.S. concerns over Japanese control over parts of the island chains. As early as 1910-11, U.S. Navy military theorists, including scholars at the Naval War College, suspected that Japan might one day threaten American possession of the Philippines and Guam. The result was the so-called War Plan Orange, assembled by Rear Admiral Raymond Rodgers. This plan, first drafted in 1911 and refined over the next twenty-five years, anticipated later Pacific operations during World War II, including a “leapfrog” campaign to seize the Marshall and Caroline islands from imperial Japan.
The U.S. Marine Corps (USMC)’s contribution to War Plan Orange has been credited largely to Lieutenant Colonel Earl Hancock “Pete” Ellis, one of its intelligence officers, who distinguished himself as an early theorist of amphibious operations. Ellis contributed most directly through his development of Operational Plan 712, “Advanced Base Operations in Micronesia,” approved as a secret “War Plan” in 1921 by his mentor USMC Commandant Major General John Archer Lejeune. In it, Ellis foresaw the island hopping campaigns of two decades later and offered detailed plans for their successful prosecution by U.S. forces. Today, the USMC maintains that “the actual American campaign for Micronesia diverged from Ellis’ plan only in areas affected by technological advances.”
Ellis’s perspicacity may seem extraordinary, and was only fully recognized in hindsight—in part because of his death in 1923 from alcoholic complications in Palau, one of the Japanese-occupied Caroline Islands which he was attempting to survey covertly. But the strength of his conclusions clearly stems from their grounding in then-unprecedentedly-systematic analysis of the island chains’ geography and potential strategic utility. Ellis devoted particular attention to “the continued occupation of the Marshall, Caroline, and Pelew [Palau] Islands by the Japanese,” which “invests them with a series of emergency bases flanking any line of communications across the Pacific throughout distance of 2300 miles.” Describing these features as “a veritable ‘Cloud’ of islands and reefs” containing “chains of low coral stalls,” he offered what for his era was an exhaustive review of their geomorphology and its implications for the operations that he believed would be necessary to wrest them from Japanese control. To this end, he offered a detailed, hierarchical strategy for American seizure of these “inter-supporting island groups” and establishment of “base facilities for the further pursuance of our operations in areas beyond.” Ellis prioritized in particular the recapturing of Guam, “which it is expected will be strongly held by the enemy as a base.”
During the Pacific War, as Ellis foresaw, the U.S. military itself had to hold the island chains it already controlled, and to penetrate fortified Japanese-held island chains. Admiral Earnest King, for instance, believed that controlling Taiwan “would let the U.S. Navy ‘put the cork in the bottle’ of the South China Sea during World War II, severing Japanese SLOCs and thus Japan’s supply of oil and raw materials.” As Vego’s map below indicates, this American exploitation of theater geometry quite literally shaped the outcome of that epic transoceanic struggle.
Emerging victorious from the Pacific War, U.S. strategists soon turned their attention to the importance of the island chains in the nascent Cold War. It was in this period that the “island chains” concept itself was developed and defined clearly. Washington’s postwar Pacific strategy yielded the earliest explicit mention of an island chains concept we have found: a 1948 Joint Chiefs of Staff study demarcating an American defensive perimeter running from the Aleutian Islands, south through occupied Japan, then through Taiwan and the Philippines.
General Douglas MacArthur played a key role in thinking through the geopolitical significance of the island chains during the early Cold War. As Naval War College scholar Toshi Yoshihara points out, MacArthur argued that the U.S. military should establish a “striking force” stationed along a “U-shaped area embracing the Aleutians, Midway, the former Japanese mandated islands, Clark air base in the Philippines, and above all, Okinawa.” In his “Message on Formosa” of 17 August 1950, MacArthur described Taiwan as “an unsinkable aircraft carrier and submarine tender ideally located to accomplish offensive strategy and at the same time checkmate defensive or counter-offensive operations by friendly forces based on Okinawa and the Philippines.” In his 1951 farewell address to Congress, MacArthur distilled his island chain thinking into its most comprehensive and forceful essence, using it as a unifying theme to inform his final policy recommendations concerning the future of American strategy vis-à-vis the Asia-Pacific. In doing so, he described the U.S. Pacific posture as being quite literally based on the central outward-projecting angle of a bastion-battle line:
“. . . the western strategic frontier of the United States lay on the littoral line of the Americas with an exposed island salient extending out through Hawaii, Midway and Guam to the Philippines. That salient proved not an outpost of strength but an avenue of weakness along which the enemy could and did attack. The Pacific was a potential area of advance for any predatory force intent upon striking at the bordering land areas.
“All this was changed by our Pacific victory, our strategic frontier then shifted to embrace the entire Pacific Ocean which became a vast moat to protect us as long as we hold it. Indeed, it acts as a protective shield for all of the Americas and all free lands of the Pacific Ocean area. We control it to the shores of Asia by a chain of islands extending in an arc from the Aleutians to the Mariannas held by us and our free allies.
“From this island chain we can dominate with sea and air power every Asiatic port from Vladivostok to Singapore and prevent any hostile movement into the Pacific. . . .
“The holding of this defense line in the western Pacific is entirely dependent upon holding all segments thereof, for any major breach of that line by an unfriendly power would render vulnerable to determined attack every other major segment. This is a military estimate as to which I have yet to find a military leader who will take exception. For that reason I have strongly recommended in the past as a matter of military urgency that under no circumstances must Formosa fall under Communist control. Such an eventuality would at once threaten the freedom of the Philippines and the loss of Japan, and might well force our western frontier back to the coasts of California, Oregon and Washington.”
However ill-advised some of MacArthur’s actions in Korea and elsewhere; and however excessively-Taiwan-centric, exaggerated, or otherwise unrealistic the above maritime domino theory might be to implement fully in practice; his island chain philosophy indeed encapsulates some important strategic thinking of the era. Such thinking unquestionably influenced Chinese strategists as they sought to make sense of their nation’s geostrategic position, the security challenges it faced, and what it might do to address them.
China’s Appropriation of the Concept
In formulating their own views on the island chains, Chinese military theorists frequently look back on American strategic ideas from the mid-twentieth century. Many Chinese sources refer to early Cold War-era statements articulating the need for a U.S. defensive perimeter in the Western Pacific, such as that proposed by MacArthur and others, including Dean Acheson and John Foster Dulles. Tracing the origin of the concept, one Chinese military scholar states: “The term ‘island chain’ originated from the proposal made by Western countries led by the United States after World War II by taking advantage of the strategic geographic locations of some special island groups in the Northwest Pacific Ocean waters to suppress and block socialist countries at the time, such as the Soviet Union and China.”
Contemporary Chinese strategic thinking related to the island chains emphasizes the early Cold War-era U.S. strategy of constructing a defensive perimeter meant to contain the Soviet Union and its Chinese ally. As we chronicle in a recent China Quarterly article, Chinese military writings frequently refer to the island chains as barriers imposed by the United States that limit China’s ability to evolve into a genuine maritime power with freedom of maneuver throughout the Western Pacific. A 2007 article in the Chinese navy’s official magazine, for instance, declares that the island chains have the power to “contain China and the Chinese navy.” Two Chinese naval strategists similarly argue that the “partially sealed-off nature of China’s maritime region has clearly brought negative effects on China’s maritime security.” Moreover, harkening back to American activities in the 1950s, contemporary Chinese writings often portray U.S. force deployments in areas such as Guam, the Philippines, and Okinawa as the result of “Cold War thinking” designed to contain China.
A similar strand of Chinese military thinking conceives of the island chains as “springboards” from which the U.S. military can conduct operations close to Chinese sovereignty claims. For instance, retired PLAN Rear Admiral Zhang Zhaozhong has identified Guam as a strategic location from which the United States can “immediately send out aircraft or dispatch submarines, in order to put power into the war zone,” referring to the Taiwan Strait.
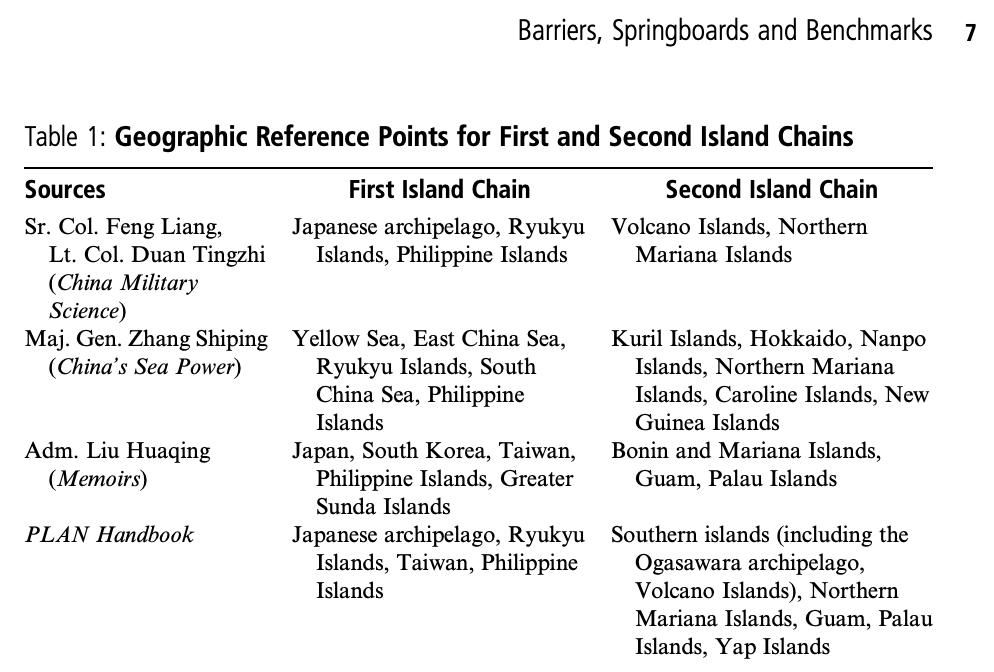
In contrast to these views of the island chains as the locus of threats posed by the U.S. military, some Chinese military theorists see the island chains more as benchmarks for Chinese military operations. This mode of thinking is most prominent among naval strategists. Admiral Liu Huaqing argued that, for the foreseeable future, most naval operations would be confined to the First Island Chain, which he defined as including Japan, South Korea, Taiwan, the Philippine Islands and the Greater Sunda Islands. But, as a long-term goal, Liu argued that China must be prepared to eventually operate out to the Second Island Chain, including the Mariana Islands, Guam and Palau. Chinese media frequently details progress towards this goal, describing in almost heroic terms the voyages of successive Chinese naval flotillas through the strategic passageways of the First Island Chain, and into more distant waters. For some, then, the island chains have become markers in China’s attempts to develop a “blue water” navy capable of performing both wartime and peacetime missions.
The Island Chains’ Enduring Relevance
Beyond the exigencies of specific planning scenarios, why do strategists from so many nations periodically fix their gaze—explicitly or implicitly—on the island chains? They do so because these long strings of land features have intrinsic geostrategic value. There is a basic geo-operational reason for this. Military platforms and their crews generally require support from appropriately-positioned terrestrial bases for their high-performance, sustained, cost-effective operation. As any glance at a globe reveals, the Pacific Ocean is vast, containing 714 million cubic kilometers of water, 50.1 percent of global seawater. It covers 165.25 million square kilometers (63.8 million square miles)—significantly more than the Earth’s total landmass of 150 million square kilometers (58 million square miles); and equivalent 46 percent of Earth’s water surface and one-third its total surface area. The rapidity and intensity of modern military operations place an additional premium on overcoming this “Tyranny of Distance” expeditiously. Basing military assets in-region, or at least enabling and supporting their deployment there, offers an unrivaled solution.
Yet the Pacific’s unparalleled expanse contains relatively few specks of land, widely dispersed. In the entire Pacific Ocean—including the home islands of Japan, the Philippines, and New Zealand; as well as Taiwan, Hainan, Papua New Guinea, and Hawaii—there are only 20 islands larger than 10,000 square kilometers (3,861 square miles). In the South Pacific (excluding Papua New Guinea), home to the majority of the ocean’s islands, the total landmass is only 551,913 square kilometers (213,095 square miles).
These factors put an inherent premium on the military value of any given Pacific feature, particularly the very few of sufficient size, resources, and human capital to host an advanced military facility. Hence, the late nineteenth century preoccupation with “coaling stations” to power the increasingly-long-range operations of the U.S. and other navies; the Imperial Japanese efforts to gain control of Pacific islands, both to enjoy their use and deny it to the United States; the protracted island hopping campaigns of the Pacific War; and the extraordinarily-rapid, -dramatic American transformation of re-captured islands such as Guam into major militarily facilities, at a cost possibly prohibitive in conditions short of world war.
To be sure, the island chains’ precise strategic value, and hence strategists’ specific emphases on them, has varied significantly as a function of changes in military technology and application—including what weapons are based on them, how far those weapons can reach, and whether it is possible to defend and supply them. This value changed significantly during the interwar period. It shifted profoundly during the Pacific War (which, among other things, highlighted the need for air defenses to protect ships and land installations and the importance of submarines in severing supply lines). Today, it is shifting greatly once more, with the advent of much longer-range strike systems (aircraft, anti-ship cruise missiles/ASCMs, land-attack cruise missiles/LACMs, conventional ballistic missiles); and defensive systems (long-range surface-to-air missiles/SAMs). These developments are dramatically increasing the range of shore-based systems versus those based on ships—a dynamic that Chinese planners have exploited deftly and systematically. This might also apply to the value of individual islands like Taiwan, which is not placed to expand China’s power projection capability significantly, but (by virtue of geography) could in theory offer a potent “springboard” for a foreign military to attack mainland China. Such theory might have accorded with empirical reality in 1980, but this is certainly much less the case today given the PLA’s ability to crater runways; attack command and control with precision strike weapons; and use long-range SAMs to attack aircraft as soon as they are airborne. In short, given today’s Chinese weapons, Taiwan is too close to mainland China to have maximum “strategic value.”
Island chains are the subject of focus as much for their exceptional vulnerability as for their exceptional capabilities, however. Their very concentration offers an enemy a conveniently-circumscribed target set. In today’s era of long-range precision strike (LRPS), the problem has become nothing short of acute. Not for nothing has China developed and deployed the world’s largest, most diverse sub-strategic conventional ballistic missile force. Beijing now has the ability to strike more islands, in more ways, more effectively; Washington and its allies must think how best to respond.
At the geopolitical level, as documented earlier, the island chains, like the region they shape geophysically, have long been regarded as important fulcrums of world affairs. Today, as the U.S. Pacific Command emphasizes,
“The 36 nations comprising the Asia-Pacific region are home to more than 50% of the world’s population…several of the world’s largest militaries, and five nations allied with the U.S. through mutual defense treaties. Two of the three largest economies are located in the Asia-Pacific. . . . The [region] includes the most populous nation in the world, the largest democracy, and the largest Muslim-majority nation. . . . The region is a vital driver of the global economy and includes the world’s busiest international sea lanes and nine of the ten largest ports. The Asia-Pacific is also a heavily militarized region, with seven of the world’s ten largest standing militaries and five of the world’s declared nuclear nations. Given these conditions, the strategic complexity facing the region is unique.”
The island chains have long been considered particularly relevant to opposing an authoritarian continental state’s attempt to dominate Eurasia, a central imperative of U.S. strategy since its ascendance to the world stage since the late nineteenth century. During the Pacific War, Tokyo—with its sweeping seizure of Chinese territory—arguably constituted precisely such a challenge. Throughout much of the Cold War, Washington mounted geopolitically-similar opposition to both Chinese and Soviet efforts to dominate Eurasia. Recently, with China’s rise and Russia’s military resurgence, at least some Western strategists perceive analogous dynamics.
In sum, in the geopolitically-vital Pacific, the relatively few desirable and available islands are disproportionately valuable for their ability to host vital military facilities. Despite their limited strategic depth and consequent growing vulnerability to LRPS weapons, they remain irreplaceable. After all, their number remains fixed—with one notable exception.
A New Island Chain?
Arguably the most interesting Pacific geostrategic development in recent years has been what might be broadly interpreted as China’s creation of a small new island chain in the South China Sea. While other neighboring coastal states have in previous years very slowly and modestly used land reclamation to augment features under their control, since 2014 Beijing has utterly surpassed them all, both qualitatively and quantitatively. China has engaged in industrial-scale dredging, reclamation, and construction to transform a set of seven Spratly submerged reefs and rocks into large artificial islands hosting a growing constellation of facilities, many militarily-relevant. Additionally, in the Paracels near Vietnam, China has further augmented features it holds, including the already-substantial Woody Island. Now, Woody Island in the Paracels and Fiery Cross and Subi Reefs in the Spratlys boast 3 km-long-runways, sufficient to accommodate all Chinese military aircraft. Mischief Reef, also in the Spratlys, has an airfield under construction that is nearly as long.
This represents an extremely rare case in history of a nation altering inconvenient facts of geography in its favor; previous Chinese geoengineering achievements included the Great Wall and the Grand Canal. Now, in the South China Sea, Beijing is literally raising from the depths a small inner island chain to outflank what it sees as foreign threats to its sovereign claims, in part from enemy forces able to utilize bases along the First Island Chain. This is the classic approach of a continental power operating along interior lines attempting to outmaneuver a maritime power operating along exterior lines—only in this instance, uniquely, projected far out to sea from artificial features. This configuration underscores a critical reality of China as a sea power: it has genuine maritime dynamism in ways that the Soviet Union and other land powers lacked, yet the core of its focus remains rooted in outstanding territorial claims within its immediate region. As such, it is poised to remain for the foreseeable future what might be termed a “land-sea hybrid” (陆海兼备) state that is developing tremendous scale and capabilities as a “maritime power” (海洋强国), while retaining a vital landward dimension as well. Given this geostrategic context, Chinese strategists will continue to place the island chains at the center of their thinking.
A Return to the Island Chains
Meanwhile, recent Chinese developments are returning foreign attention to the island chains. In the context of growing Chinese military capabilities and the perception of increasing Chinese assertiveness in the Western Pacific, Japanese and American strategists are once again thinking through the potential strategic and operational value of the island chains. Japan’s 2010 National Defense Planning Guidance articulated a “dynamic defense force” concept that places greater emphasis on air and ballistic missile defense in its southwestern islands. More recently, citing Japanese military officials, Reuters reports that Tokyo is responding to perceived Chinese threats by reinforcing islands between mainland Japan and Taiwan with anti-ship and anti-aircraft missile batteries. This is intended as “Joint Dynamic Defense,” a Japanese version of China’s “anti-access/area-denial” strategy designed to deter Chinese aggression within the First Island Chain. According to Satoshi Morimoto, a former Japanese defense minister, “In the next five or six years, the first island chain will be crucial in the military balance between China and the U.S.-Japan [alliance].”
Some U.S. military strategists are also reevaluating the importance of the island chains in light of China’s military development. In 2012 U.S. National Defense University scholar T.X. Hammes published a paper that based a military strategy on defending the First Island Chain, denying China’s use of the waters inside it, and dominating the waters outside it. In a 2014 monograph published by the Center for a New American Security, the Naval War College’s Toshi Yoshihara recommended a strengthening of defenses along the First Island Chain to support the U.S.-Japan alliance. In Yoshihara’s words, “the prospects of an impenetrable island chain would play on China’s nightmare scenario that the PLAN could be shut out of the most direct routes to the high seas, lending Japan a psychological edge.” In a 2015 Foreign Affairs article, Andrew Krepinevich of the Center for Strategic and Budgetary Assessments likewise proposes strengthening the First Island Chain in order to “deny Beijing the ability to achieve its revisionist aims through aggression or coercion.”
Beijing’s advances in longer-range ballistic and cruise missile technology also pose significant dangers to more distant islands, such as the U.S. strategic hub of Guam. This has, in turn, led scholars at RAND and elsewhere to explore concepts such as deception and dispersal that can be used to defend air bases across the Asia-Pacific from potential Chinese threats.
In the coming years, it is likely that Chinese, American and Japanese strategists—in addition to those from other maritime Asian states—will give concurrent attention to the role that the island chains can play in achieving national military objectives. Chinese strategists will increasingly focus on perceived vulnerabilities of U.S. and allied forces along the island chains, while the latter will consider how forces can be dispersed and hardened so as to deter Chinese aggression. Such strategic and operational calculations will be only the latest in a long line of thinking stretching back to the early twentieth century. How that thinking evolves could leave an indelible mark on the strategic balance in the twenty-first century.
Andrew S. Erickson, Professor of Strategy in the China Maritime Studies Institute at the Naval War College, blogs at www.andrewerickson.com. Joel Wuthnow is a Research Fellow in the Center for the Study of Chinese Military Affairs at the National Defense University. The views expressed are their own and do not reflect the official policy or position of the Department of Defense or the U.S. government. They thank Phillip C. Saunders and T.X. Hammes for valuable suggestions.
RELATED MEDIA INTERVIEW:
Christopher P. Cavas, “Powers Jockey for Pacific Island Chain Influence,” Interview of Andrew S. Erickson, Defense News, 1 February 2016.
Pacific Island Chains Measure Regional Influence
WASHINGTON — The extensive chains of Pacific islands ringing China have been described as a wall, a barrier to be breached by an attacker or strengthened by a defender. They are seen as springboards, potential bases for operations to attack or invade others in the region. In a territorial sense, they are benchmarks marking the extent of a country’s influence.
“It’s truly a case of where you stand. Perspective is shaped by one’s geographic and geostrategic position,” said Andrew Erickson, a professor with the China Maritime Studies Institute at the Naval War College.
“Barriers is a very Chinese perspective,” said Erickson. “It reflects a concern that foreign military facilities based on the islands may impede or threaten China’s efforts or influence.”
The springboard concept can work offensively or defensively.
“Many Chinese writings express concerns that the chains can be used as springboards for projection and forces against China. But some sources imagine future contingencies where China itself might have growing influence and presence, with Taiwan being most relevant in that regard,” Erickson said.
“Benchmarks speak to the idea that as China increasingly engages in blue-water operations and limited forms of power projection, having more ships through the first island chain offers a set of milestones by which the People’s Liberation Army Navy – or PLAN – can measure its growing presence and capabilities.”
Senior officials and analysts in the West frequently refer to the first and second island chains ringing China to describe both the region’s geography and predict Chinese intentions. Erickson, in a new paper co-authored with Joel Wuthnow of the National Defense University and published in The China Quarterly, carried out a comprehensive, five-year examination of Chinese literature to determine how mainland China views the chains. He reported that the idea originated in the west during the Cold War – Chinese sources often credit 1950s US Secretary of State John Foster Dulles as the concept’s progenitor.
But the notion, Erickson pointed out, isn’t new – it derives from the region’s physical characteristics. Still, the chains have risen in political thinking to become benchmarks that in many ways define the field of play as China’s regional maritime power expands.
“You won’t find in a single authoritative source a precise official consensus on what the chains mean,” Erickson said. “But if you look at a variety of Chinese sources you see a larger pattern that speaks to Chinese concerns about foreign sources having influence over the region and over outstanding disputes. This is not a figment of China’s geostrategic imagination.”
Those concepts play out in numerous fashions, from the weapons China develops to the kinds of exercises and operations the military carries out.
“It looks like we’re seeing a broad-based Chinese effort to become familiar with a variety of different ways to get through the island chains,” Erickson noted. “It’s not hard to imagine that China would want to develop experience with as many different ways as possible to get through the chains.”
China’s development of short-range ballistic missiles is also related to its thinking about the first island chain, Erickson said.
“The vast majority of those weapons appear targeted at Taiwan, which many Chinese authorities see as a key point in the first island chain,” he said. “The vast majority of the missiles I’ve mentioned are designed to target very specific land bases. It’s only very recently that we see a small but growing portion of conventional ballistic missiles developed with the intent of being able to threaten US and perhaps allied naval vessels.”
The Chinese Navy, Erickson pointed out, operates the world’s largest conventional submarine missile force. “The vast majority of those missiles having the right range to appear to be targeted at various US and allied military bases in the region, almost all of which are somewhere along the first island chain.”
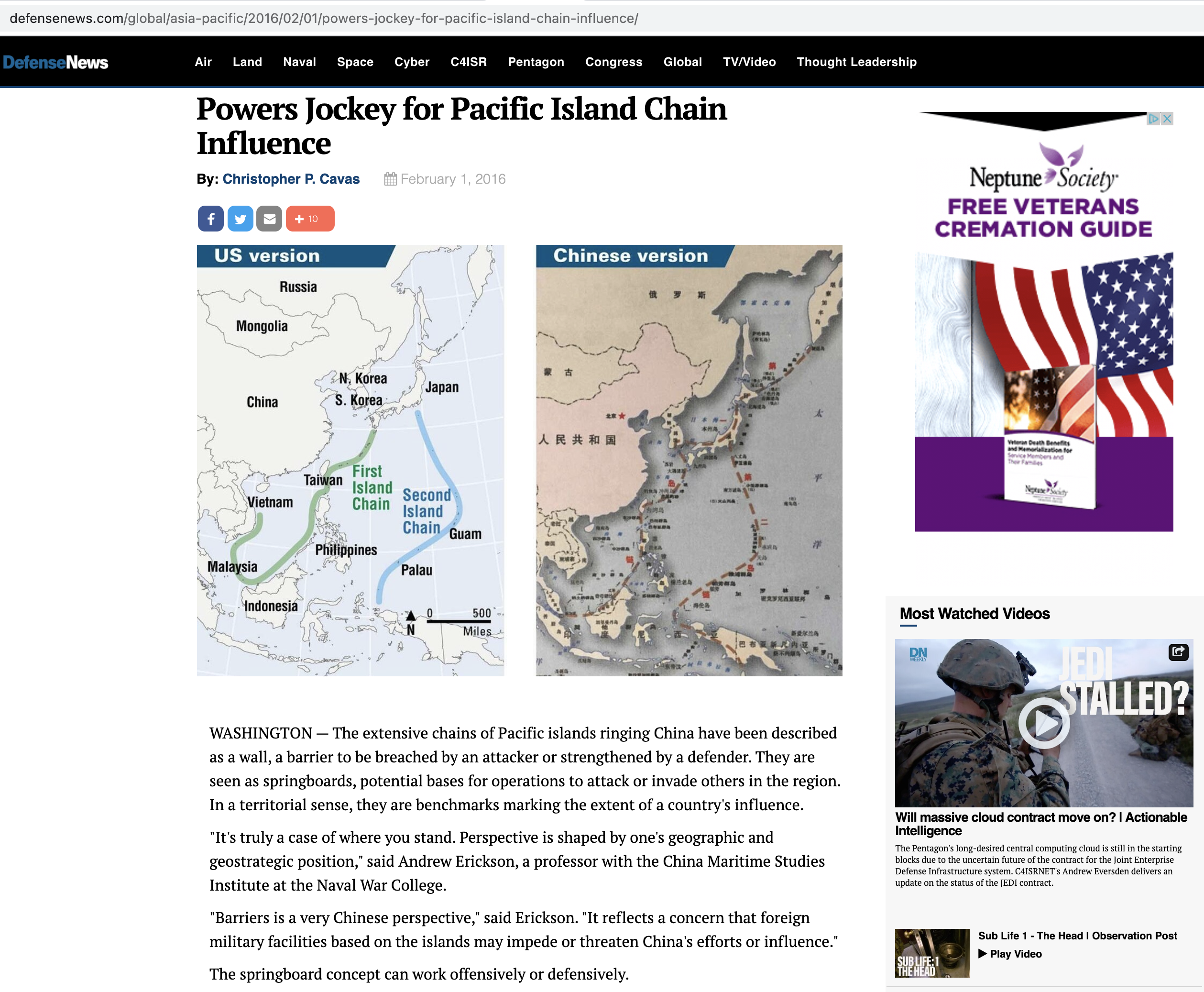
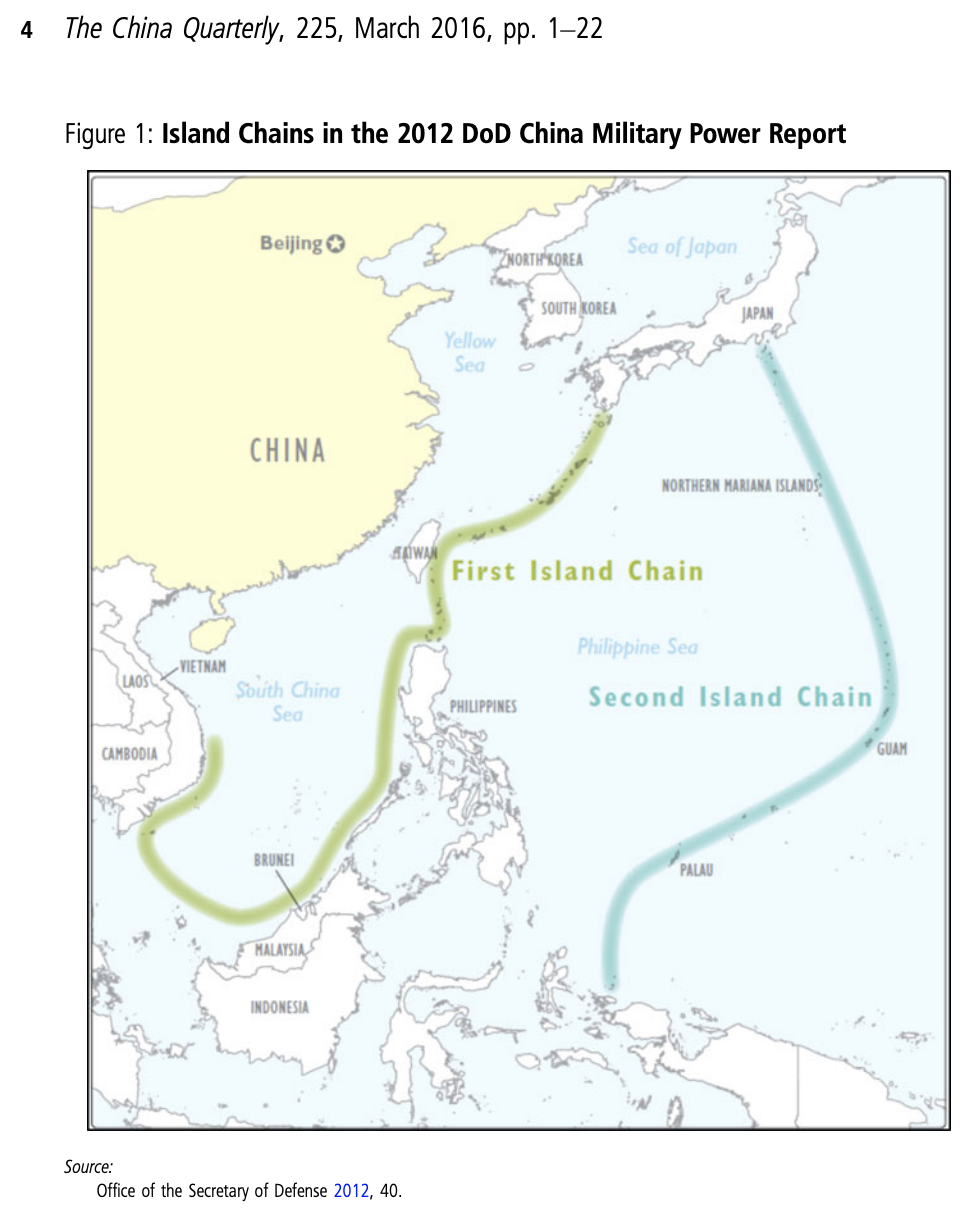
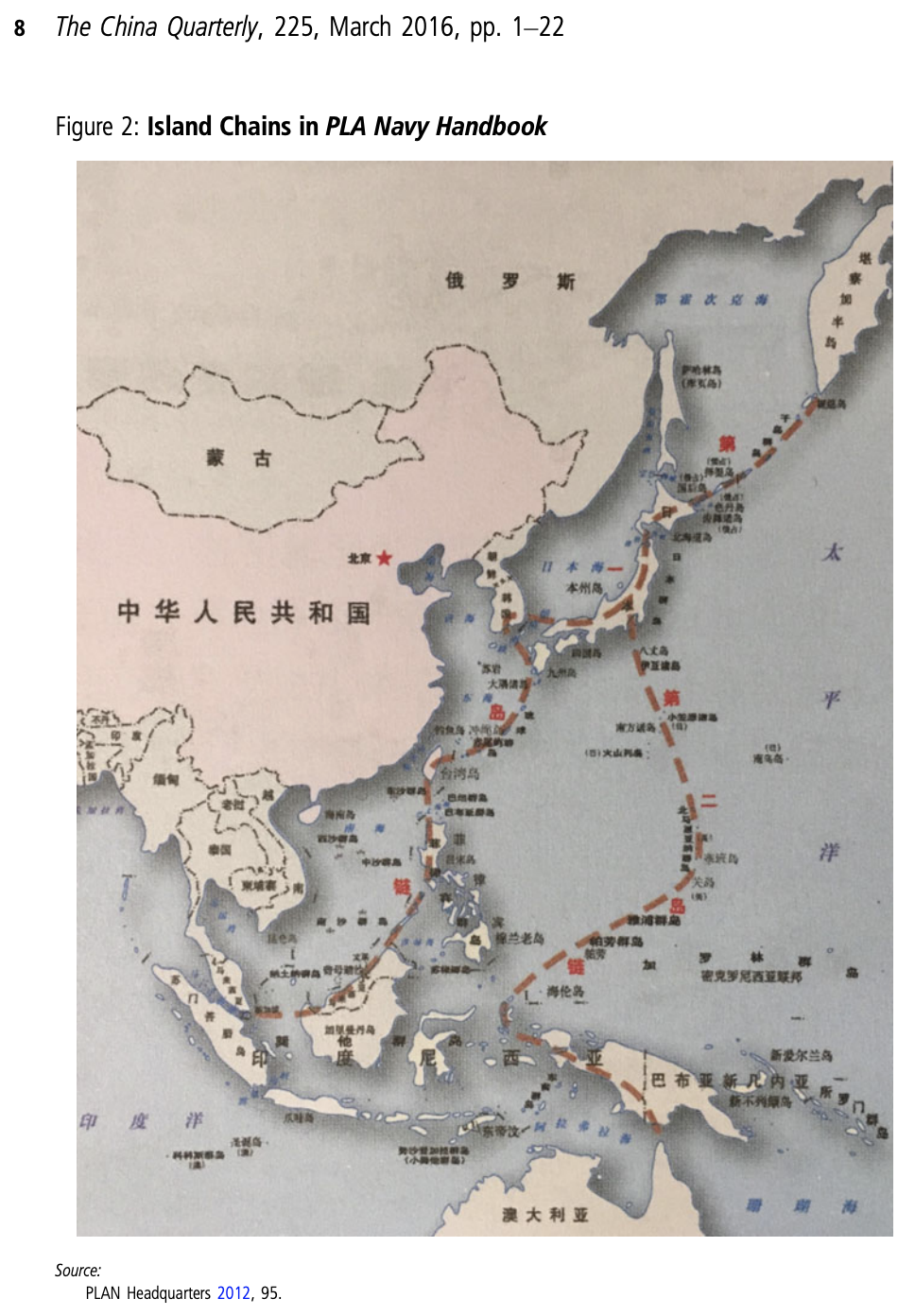
Subtle differences in how the US and China view the chains are evident, Erickson said, in maps produced by the US Defense Department and the Chinese Navy. The Pentagon map, he noted, “doesn’t show South Korea as part of the chain, but the PLAN book very much does show it as belonging to the first island chain.”
Another key difference is in how the Chinese depict the chains joining up in Japan, stretching across the Sea of Okhotsk to the southern tip of Russia’s Kamchatka peninsula – a feature absent from the US map.
The differences indicate different ways of thinking about the chains, Erickson said.
“I don’t think the DoD map is the best possible expression about how the Chinese Navy thinks about the chains – the PLAN map is,” he noted. “This is a case of differences in nuance, not in fundamental differences. I don’t think DoD has gotten this wrong, it’s just a different focus.”
China’s recently aggressive island-building strategy, Erickson observed, is related to the springboard and barrier concepts.
“The chain traditionally has made use of existing geography, but you could argue that China is now making its own island chain – as a springboard for itself and to create a barrier to others,” Erickson said. “I haven’t yet seen Chinese sources that refer to this artificial island construction development as an island chain type thing, but if we look at it conceptually we’re really talking about similar things. That’s one reason I think there’s so much US, regional and allied concern about Chinese activities in the South China Sea.”
Among countries in the region, Russia and Korea are less involved with island chain concepts. “Russia has bigger geostrategic problems to worry about,” Erickson said, while South Korea “by necessity is so focused on security threats from the north that that is the fundamental factor affecting their nation’s geostrategic orientation.”
Japan, across the seas from Russia and Korea, is in a different position.
“In many ways Japan is as central to island chain thinking as one can get,” Erickson said. “Japan constitutes the largest portion of the first and second chains as any other nation. It is a nation of more than 6,000 islands. It is as close to a natural sea power as a nation can get.”
Before World War II, Japan also described the western Pacific in island chain terms.
“Back when imperial Japan was trying to gain control of the first, second and even a third chain – the Aleutians – there was a concern that if Japan didn’t control the Philippines, Guam and Hawaii the Americans would, to Japan’s geostrategic detriment,” said Erickson. “At the outset of World War II, Japan made an extraordinary effort to use part of the chains as a springboard, and they were indeed benchmarks of Japanese military progress. That was only halted then the US turned island-hopping in the other direction.”
“Today, Japan is concerned about Chinese attempts to influence and control areas and to develop weapon systems vis-a-vis these island chains,” Erickson added. “And there’s a lot of Japanese concern about ongoing Chinese efforts to penetrate the chains using increasingly powerful and complex groups of naval vessels. I think Japan feels very much connected to these island chains. As China looks to the chains and aspires to do things, I think Japan feels very targeted by that, it feels it very acutely.”
Taiwan, unsurprisingly, often stands out in the attention it receives in Chinese writings.
“Many Chinese sources emphasize their view of Taiwan’s status as a key node on the first island chain,” Erickson said. “Some Chinese sources see this not only as a springboard against mainland China, but a number of sources express aspirations of eventually [bringing the island] under mainland control, perhaps in a very robust fashion that would allow for some form of Chinese-controlled military facilities. We see discussion of ports, particularly on the east coast of Taiwan, allowing for China to conclusively break out of the confines of the first island chain once and for all.”
“I see no other part of an island chain that is really in the category of what some Chinese strategists ultimately aspire to control and own themselves,” Erickson said. “That definitely sets Taiwan apart.”
And while most attention is focused on the first island chain running south along the eastern edge of the South China Sea, the significance of the second chain, which includes the US territory of Guam, could grow.
“A number of Chinese sources see this as a rear staging area for US and allied forces,” Erickson said.
“But the second island chain will grow in China’s geostrategic thinking. As China continues to send naval forces afield, it will be a benchmark.”
Over time, he added, “China can do more to hold Guam and other parts of the second island chain at risk.”
HERE IS THE JOURNAL ARTICLE REFERENCED IN THE ABOVE ARTICLE AND INTERVIEW:
Andrew S. Erickson and Joel Wuthnow, “Barriers, Springboards and Benchmarks: China Conceptualizes the Pacific ‘Island Chains’,” The China Quarterly 225 (March 2016): 1-22.
Barriers, Springboards and Benchmarks: China Conceptualizes the Pacific “Island Chains”
Andrew S. Erickson, US Naval War College, Newport, RI; and Joel Wuthnow, US National Defense University, Washington, DC
Abstract
US government reports describe Chinese-conceived “island chains” in the Western Pacific as narrow demarcations for Chinese “counter-intervention” operations to defeat US and allied forces in altercations over contested territorial claims. The sparse scholarship available does little to contest this excessively myopic assertion. Yet, further examination reveals meaningful differences that can greatly enhance an understanding of Chinese views of the “island chains” concept, and with it important aspects of China’s efforts to develop as a maritime power. Long before China had a navy or naval strategists worthy of the name, the concept had originated and been developed for decades by previous great powers vying for Asia-Pacific influence. Today, China’s own authoritative interpretations are flexible, nuanced and multifaceted – befitting the multiple and sometimes contradictory factors with which Beijing must contend in managing its meteoric maritime rise. These include the growing importance of sea lane security at increasing distances and levels of operational intensity.
摘要
美国政府报告把中国设想的西太平洋 “岛链” 概念描述为中国军队为在有关领土争端的 “反干涉”作战中试图打败美国和盟国部队而设立的狭窄的界线。寥寥无几的相关研究对这个过于短视的看法也没有提出不同意见。然而, 进一步的分析却发现此概念有迥然不同的含义。这些含义能大大增强我们对中国为发展成为一个海洋大国所做出的努力的理解。这个概念是在中国有一个现代的海军或海军战略家之前由其他有影响力的大国为争夺亚太地区的影响力而发展起来的。如今, 中国对此概念的权威解释显示出其灵活性, 微妙性和多面性。这些解释特征恰恰能与北京在管理其海上崛起过程中许多有时是相互矛盾的因素相适应。这些因素包括由于不断增大距离和活动强度所导致的海上通道安全日益增长的重要性。
Keywords
China; island chain; strategy; military; maritime; navy
关键词
中国; 岛链; 战略; 军事; 海事; 海军
Footnotes
* These are the authors’ personal views, and not those of their respective institutions. For comments on earlier drafts, the authors thank Dennis Blasko, M. Taylor Fravel, Ryan D. Martinson, Ivan Rasmussen, Al Willner, and three anonymous reviewers.
***
Outside observers naturally seek to understand the geostrategic basis for China’s rapid maritime development. Accordingly, US scholarship and government documents regularly make assertions about Chinese military views of Western Pacific “island chains” (daolian 岛链). In many cases, the argument is that the People’s Liberation Army (PLA) uses the island chains as benchmarks for a potential “counter-intervention” campaign directed against US and allied forces in the region. However, these analyses rarely document evidence from PLA sources. This raises important questions: how do Chinese strategists themselves define “island chains,” and how do they assess them operationally and strategically?
Drawing on manifold underutilized Chinese sources, we contend that the island chains concept is foreign in origin but adopted and reinterpreted in China, and that authoritative Chinese interpretations are flexible, nuanced and multifaceted. Geographically, Chinese writings offer varying definitions of the island chains, with some considerably more expansive than others. More importantly, Chinese sources offer diverse perspectives on the island chains’ operational and strategic significance. In particular, various Chinese authors assert that the island chains are (1) barriers that China must penetrate to achieve freedom of manoeuvre in the maritime domain; (2) springboards for power projection by whomever controls a given island chain; and (3) benchmarks for the advancement of Chinese maritime and air force projection in the Asia-Pacific. In each of these respects, the discourse on the island chains provides valuable insight into how the PLA is thinking about the challenges and opportunities facing China as it seeks to become a maritime power.
This article is organized into five sections. The first discusses foreign analyses of the concept of island chains, and suggests that many of these sources focus rigidly on counter-intervention issues. The following section addresses the origins and historical significance of the island chains concept. The article then examines Chinese views of the geographic attributes of the island chains before considering how Chinese military analysts interpret their operational and strategic significance. The final section discusses the implications for China’s naval development, and for that of the US and its allies. …
References
- Acheson, Dean. 1951. “Remarks by the secretary of state (Acheson) before the National Press Club, Washington, January 12, 1950.” In Dennett, Raymond and Turner, Robert (eds.), Documents on American Foreign Relations, Vol. 12: January 1–December 31, 1950. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press, 426–433. Google Scholar
- Bai, Yanlin. 2007. “Daolian shang de shijie haijun” (The world navies on the island chains). Dangdai haijun 10(October), 10–20. Google Scholar
- Bi, Xinglin (ed.). 2002. Zhanyi lilun xuexi zhinan (Campaign Theory Study Guide). Beijing: Guofang daxue chubanshe. Google Scholar
- Cheng, Dean. 2011. “Sea power and the Chinese state: China’s maritime ambitions.” Heritage Foundation Backgrounder Report No. 2576, 11 July, http://www.heritage.org/research/reports/2011/07/sea-power-and-the-chinese-state-chinas-maritime-ambitions. Accessed 21 December 2015. Google Scholar
- Cliff, Roger. 2011. “Anti-access measures in Chinese defense strategy.” Testimony before the US–China Economic and Security Review Commission, Washington, DC, 27 January. Google Scholar
- Cole, Bernard. 2010. The Great Wall at Sea: China’s Navy in the Twenty-First Century (2nd ed.). Annapolis, MD: Naval Institute Press. Google Scholar
- Cole, Bernard. 2014. “Island chains and naval classics.” US Naval Institute Proceedings 140(11), 68–73. Google Scholar
- Dan, Jie, and Ju, Lang. 2005. “Fei xiang Zhongguo de ‘ni huo’ he ‘xiong’” ([Russian] “Backfire” and “Bear” [Strategic Bombers] to fly to China). Jianzai wuqi March, 12–16. Google Scholar
- Ding, Zhaolun. 2011. “Qiaokai weilai haizhan zhisheng zhi men” (Knock open the gate of winning future sea battles), Renmin haijun, 11 March. Google Scholar
- Du, Jingchen. 2010. “Ba yuanhai dayang dangzuo ‘lian bing chang’” (Regard the distant seas and oceans as training areas), Renmin haijun, 18 May. Google Scholar
- Feng, Liang, and Duan, Tingzhi. 2007. “Zhongguo haiyang diyuan anquan tezheng yu xin shiji haishang anquan zhanlüe” (Characteristics of China’s sea geostrategic security and sea security strategy in the new century). Zhongguo junshi kexue 1, 22–29. Google Scholar
- Flynn, Michael. 2014. “Annual threat assessment.” Statement before the Senate Armed Services Committee, Washington, DC, 11 February. Google Scholar
- Fravel, M. Taylor, and Christopher, Twomey. 2015. “Projecting strategy: the myth of Chinese counter-intervention.” The Washington Quarterly 37(4), 171–187. CrossRef | Google Scholar
- Friedman, B.A. 2015. 21st Century Ellis: Operational Art and Strategic Prophecy for the Modern Era. Annapolis, MD: Naval Institute Press. Google Scholar
- Fuell, Lee. 2014. “Broad trends in Chinese air force and missile modernization.” Testimony presented to the US–China Economic Security Review Commission, Washington, DC, 30 January. Google Scholar
- Guoji zhanwang. 2005. “Meiguo yingpai renwu zai fang kuangyan – toushi Meiguo kongzhong daji Zhongguo jihua” (Members of the US “hawk faction” rave again: a perspective on a US plan to attack China from the air). Guoji zhanwang 9, 27–28. Google Scholar
- Hammes, T.X. 2012. “Offshore control: a proposed strategy for an unlikely conflict.” Strategic Forum 278, 1–14. Google Scholar
- Hattendorf, John, Simpson, B. Mitchell and Wadleigh, John R.. 1984. Soldiers and Scholars: The Centennial History of the US Naval War College. Newport, RI: Naval War College Press. Google Scholar
- Holmes, James. 2011. “Integrated Chinese saturation attacks: Mahan’s logic, Mao’s grammar.” In Erickson, Andrew and Goldstein, Lyle (eds.), Chinese Aerospace Power: Evolving Maritime Roles. Annapolis, MD: Naval Institute Press, 407–422. Google Scholar
- Huang, Alexander. 1994. “The Chinese navy’s offshore active defense strategy: conceptualization and implications.” Naval War College Review 47(3), 7–32. Google Scholar
- Hui, Zhu. 2009. Zhanlüe kongjun lun (Strategic Air Force). Beijing: Lantian chubanshe. Google Scholar
- Kaplan, Robert. 2010. “The geography of Chinese power.” Foreign Affairs 89(3), 22–41. Google Scholar
- Krepinevich, Andrew F. Jr. 2015. “How to deter China: the case for archipelagic defense.” Foreign Affairs 94(2), https://www.foreignaffairs.com/articles/china/2015-02-16/how-deter-china. Google Scholar
- Li, Yihu. 2007. “Cong hailu erfen dao hailu xichou – dui Zhongguo hailu guanxi de zai shenshi” (Sea and land power: from dichotomy to overall planning – a review of the relationship between sea and land power). Xiandai guoji guanxi 8, 1–7. Google Scholar
- Liang, Fang. 2011. Haishang zhanlüe tongdao lun (On Maritime Strategic Access). Beijing: Shishi chubanshe. Google Scholar
- Liu, Huaqing. 2004. Liu Huaqing huiyi lü (Memoirs of Liu Huaqing). Beijing: Jiefangjun chubanshe. Google Scholar
- Lou, Douzi. 2004. “Tizhi bianzhi tiaozheng hou, kan haijun kongjun de bu shi (yi)” (Looking at navy and air force dispositions following establishment restructuring (part 1)), Jiefangjun bao, 14 July. Google Scholar
- Ma, Guangwu. 2011. Zhongguo heping fazhan zhong de qiangjun zhanlüe (The Strong Army Strategy in China’s Peaceful Development). Beijing: Junshi kexue chubanshe. Google Scholar
- MacArthur, Douglas. 1951. “Old soldiers never die…” Typescript speech for address given 19 April, Library of Congress, http://www.loc.gov/exhibits/treasures/trm048.html. Accessed 10 December 2015. Google Scholar
- McDevitt, Michael. 2011. “The PLA navy’s antiaccess role in a Taiwan contingency.” In Saunders, Phillip C., Yung, Christopher, Swaine, Michael and Yang, Andrew Nien-dzu (eds.), The Chinese Navy: Expanding Capabilities, Evolving Roles. Washington, DC: NDU Press, 191–214. Google Scholar
- Miller, Edward. 1991. War Plan Orange: The US Strategy to Defeat Japan, 1897–1945. Annapolis, MD: Naval Institute Press. Google Scholar
- Muller, David. 1983. China as a Maritime Power. Boulder, CO: Westview Press. Google Scholar
- Nathan, Andrew J. 1996. “China’s goals in the Taiwan Strait.” The China Journal 35, 87–93.CrossRef | Google Scholar
- Office of the Secretary of Defense. 2011. Annual Report to Congress: Military and Security Developments Involving the People’s Republic of China. Washington, DC: DoD. Google Scholar
- Office of the Secretary of Defense. 2012. Annual Report to Congress: Military and Security Developments Involving the People’s Republic of China. Washington, DC: DoD. Google Scholar
- Office of the Secretary of Defense. 2015. Annual Report to Congress: Military and Security Developments Involving the People’s Republic of China. Washington, DC: DoD. Google Scholar
- Peattie, Mark. 1988. Nan‘yō: The Rise and Fall of the Japanese in Micronesia, 1885–1945. Honolulu: University of Hawaii Press. Google Scholar
- Peng, Guangqian, and Yao, Youzhi (eds.). 2005. The Science of Military Strategy. Beijing: Military Science Press. Google Scholar
- PLAN Headquarters. 2012. Zhongguo haijun junren shouce (Handbook of PLA Navy Personnel). Beijing: Haichao chubanshe. Google Scholar
- Qingnian cankao. 2012. “Zhongguo haijun mouhua pojie ‘daolian fengsuo’” (China’s navy plots to break through the “island chain blockade”), 31 October. Google Scholar
- Run, Jiaqi. 2014. “Zhuanjia cheng Zhongguo junshi liliang poshi Meiguo cong diyi daolian xiang hou shousuo” (Experts say China’s military power has forced the United States to retreat from the First Island Chain), Renmin wang, 8 October. Google Scholar
- Sharman, Christopher H. 2015. “China moves out: stepping stones toward a new maritime strategy.” China Strategic Perspectives 9, 1–60. Google Scholar
- Swenson-Wright, John. 2005. Unequal Allies? United States Security and Alliance Policy toward Japan, 1945–1960. Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press. Google Scholar
- US Department of State. 1948. Foreign Relations of the United States, 1948. Washington, DC: US Government Printing Office. Google Scholar
- Vego, Milan. 1992. Soviet Naval Tactics. Annapolis, MD: Naval Institute Press. Google Scholar
- Vego, Milan. 2014. Major Fleet-versus-Fleet Operations in the Pacific War, 1941–1945. Newport, RI: Naval War College Press. Google Scholar
- Wachman, Alan. 2007. Why Taiwan? Geostrategic Rationales for China’s Territorial Integrity. Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press. Google Scholar
- Wang, Jing (ed.). 2004. “Mei hangmu zai Taiwan zhouwei yanxi shenme (er)” (What exercises are the US aircraft carrier conducting around Taiwan? Part 2), CCTV International, 19 June. Google Scholar
- Wang, Weixing, and Teng, Jianqun. 2000. “Air-launched cruise missiles are hanging at Asia’s door,” Jiefangjun bao, 6 September, 12. Google Scholar
- Whitney, Courtney. 1956. MacArthur: His Rendezvous with History. New York: Knopf. Google Scholar
- Willard, Robert. 2011. “Statement of Admiral Robert F. Willard, US Navy.” Statement before the House Armed Services Committee, Washington, DC, 6 April. Google Scholar
- Wu, Qingli, and Xie, Jingsheng. 2004. “Toushi Meijun quanqiu junli da tiaozheng” (Analysis of global force readjustment by the US military), Jiefangjun bao, 1 September, 12. Google Scholar
- Xu, Changyin. 2010. “Zhandou jianting biandui yuanhang zonghe baozhang wenti qietan” (Preliminary discussion on issues in comprehensive support of warship formations during long-distance voyages), Renmin haijun, 6 December. Google Scholar
- Xu, Qi. 2004. “21 shiji chu haishang diyuan zhanlüe yu Zhongguo haijun de fazhan” (Maritime geostrategy and the development of the Chinese navy in the early 21st century). Zhongguo junshi kexue 59(4), 75–81. Google Scholar
- Xu, Xikang. 2011. “Yi Liu Huaqing siling de haijun zhanlüe” (Recalling Commander Liu Huaqing’s naval strategy), Zhongguo shehui kexue bao, 20 June. Google Scholar
- Yu, Yang, and Qi, Xiaodong. 2005. “Meijun jidi da tiaozheng: miaozhun ‘xian fazhi ren’ bai bing bu zhen” (Major realignment of US military bases: deployment aimed at launching “preemptive strikes”), Zhongguo guofang bao, 19 April, 2. Google Scholar
- Zhang, Qingbao, and Lin, Xiaoying. 2013. “Zheili de diqing bu jia yinhao” (Here, the enemy situation is no longer in quotation marks), Renmin haijun, 13 May. Google Scholar
- Zhang, Shiping. 2009. Zhongguo haiquan (China’s Sea Power). Beijing: Renmin ribao chubanshe. Google Scholar
- Zhongguo guoji guanxi yanjiuyuan. 2005. Guoji zhanlüe yu anquan xingshi pinggu 2004–2005 (Review of the International Strategic and Security Situation 2004–2005). Beijing: Shishi chubanshe. Google Scholar
- Zhongguo junshi kexue yuan. 2013. Zhanlüe xue (Science of Strategy). Beijing: Junshi kexue chubanshe. Google Scholar
- Zu, Ming. 2006. “Meiguo zhu xi taiping diqu haijun bingli bushu yu jidi tixi shiyitu” (A schematic diagram of the US naval forces deployed and system of bases in the Western Pacific). Jianchuan zhishi 2(January), 24. Google Scholar
- Zuo, Liping. 2013. “Hangmu biandui chicheng hai zhangchang de daguo de zhong jian” (Carrier battle group gallops to the sea battlefield, is the strong sword of a great nation), Renmin haijun, 3 December. Google Scholar